low end tidal co2 pulmonary embolism
To evaluate whether EtCO2 measurement can be used at the bedside to exclude pulmonary embolism PE. The authors aimed to define the optimum ETCO2 to conclusively exclude a pulmonary embolic event.

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
However there was no significant difference between pulmonary embolism and hypovolemia.

. Identifying reversible causes of cardiac arrest is challenging. One hundred consecutive patients with suspected pulmonary embolisms PEs were enrolled over 6 months in 2012. 1 that etCO2 can dist.
Lepage Y Girard D Blaise G. Identifying reversible causes of. Ad Get Info On An Rx Option To Treat Lower The Risk Of Recurrent DVTPE Blood Clots.
Identifying reversible causes of cardiac arrest is challenging. 1 The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism poses a diagnostic challenge in the emergency department ED despite. We analysed the charts of 12 patients who presented with clinical shock and had end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 and arterial CO 2 partial pressure PaCO 2 measurements.
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Pulmonary embolism PE has been labelled as one of the leading causes of cardiovascular death in the Western World 1 and still today more than 40000 patients in Germany and 200000 in the USA die of acute PE each year.
Request PDF A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism Introduction. We aimed to define the optimal P ETCO2 level to exclude PE in patients evaluated for possible thromboembolism. Continuous pulmonary arterial pressure can be used to evaluate for gas embolism.
15 mg Hg CO2 compared to that of the low. Pulmonary embolism PE is associated with approximately 100000 deaths per year in the United States and the incidence of deep vein thrombosispulmonary embolism in the United States is estimated at more than 350000 cases annually. Visit The Official Patient Site For Additional Information About DVTPE Blood Clots.
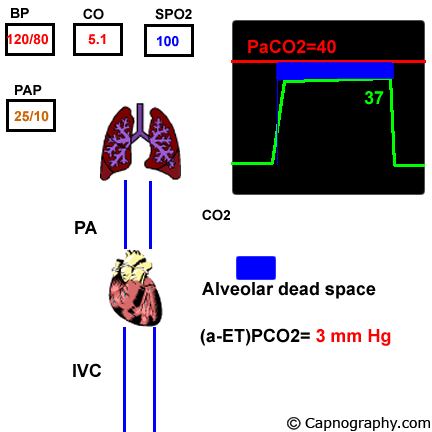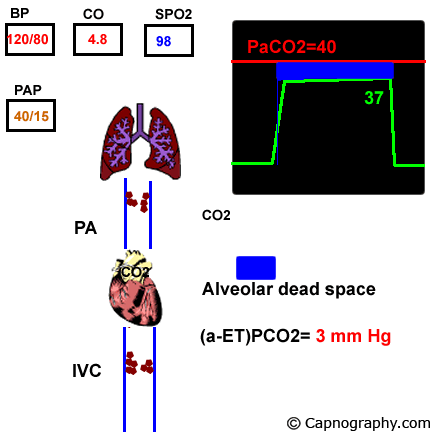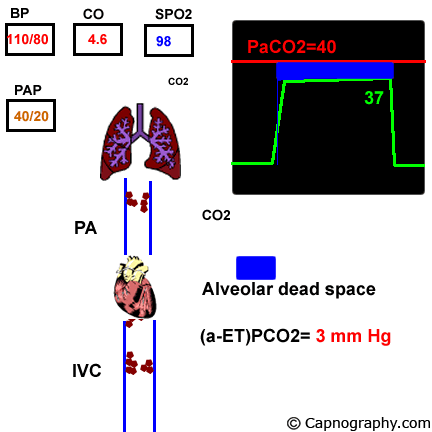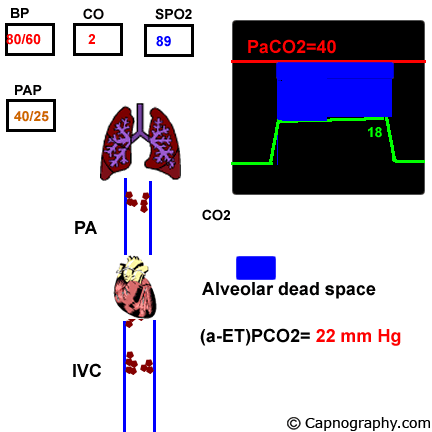
Symptoms demographic date Well. Pulmonary embolism increases alveolar dead space resulting in low end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 relative to arterial CO 2 PaCO 2 tensionThus a low EtCO 2 PaCO 2 ratio during resuscitation may be a sign of pulmonary embolism. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO2 etCO2 and tested two hypotheses.
P ETCO2 was measured within 24 h of. Venous carbon dioxide embolism in pigs. A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism.
At the third rhythm analysis EtCO 2 levels were significantly lower when cardiac arrest was caused by pulmonary embolism than by primary arrhythmia hypoxia and hyperkalaemia. Role of end-tidal CO2 as a screening tool Clin Med. 298 patients were enrolled over 6 months at a single academic centre.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 can represent dead space ventilation. End-tidal CO 2 and blood gas values. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is often missed.
Riaz I Jacob B Pulmonary embolism in Bradford UK. Results In cases with pulmonary embolism-related shock n 3 the gradient between PaCO 2 and EtCO 2 was increased 37 vs 02 mmHg. In contrast PaCO 2 levels were higher with pulmonary.
Sudden decrease or loss of end-tidal CO2 suggests a drastic decrease in cardiac output due to gas embolism. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. This was a prospective diagnostic study set in a British acute medical admissions ward.
Thus a low EtCO 2 PaCO 2 ratio during resuscitation may be a sign of pulmonary embolism. End tidal carbon dioxide tension P ETCO2 is a surrogate for dead space ventilation which may be useful in the evaluation of pulmonary embolism PE. Pulmonary embolism increases alveolar dead space resulting in low end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 relative to arterial CO 2 PaCO 2 tension.
ArticleAagaard2018ALE titleA low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism authorRasmus Aagaard and Bo Lofgren. However hospital mortality rates can fall from as high as 30 to 8 2 when diagnosis and treatment are properly provided. 2014 Apr14 2 Objective.
An evaluation of end-tidal carbon. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is often missed.
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Basics Of Waveform Capnography Waveform Capnography Grepmed

Pulmonary Thrombo Embolism Capnography

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Evaluation Of Suspected Pulmonary Embolism Utilizing End Tidal Co2 And D Dimer The American Journal Of Surgery